constant rate test stress relaxation creep test fatigue test|transient creep vs constant : manufacture 1.1 Overview. Creep is defined as a time-dependent plastic deformation that occurs at constant stress and temperature. It is due to the inelastic response of loaded materials at high .
webReload page. 75K Followers, 1,050 Following, 89 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Kesia Lins (@kesialins2)
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBVoos. Oriente Médio. Israel. Compare voos de Israel em centenas de fornecedores. Encontre o mês e até o dia do ano mais baratos para voar. Reserve a melhor tarifa sem .
A creep test, sometimes referred to as a stress-relaxation test, is used to determine the amount of deformation a material experiences over time while under a continuous tensile or compressive load at a constant temperature.If a creep test is carried to its conclusion (that is, fracture of the test specimen), often without precise measurement of its dimensional change, then this is called a stress rupture test (see . Creep testing measures the gradual rate of deformation of a material under constant load and temperature conditions. Fatigue testing, on the other hand, involves subjecting a material or structure to cyclic loading.The creep test, also known as the stress relaxation test, is a destructive way of evaluating a material’s durability and thermal stability. A creep test is one in which the specimen is heated for an extended period and supplied with a constant .
The creep test, in some instances referred to as stress relaxation test, is a destructive materials testing method for determination of the long-term strength and heat resistance of a material. .1.1 Overview. Creep is defined as a time-dependent plastic deformation that occurs at constant stress and temperature. It is due to the inelastic response of loaded materials at high .A series of creep tests at constant stress on an ~-Cu alloy gave the following results for the minimum creep strain rate. 83Creep deformation is normally studied by applying either a constant load or a constant true stress to a material at a sufficiently high homologous temperature so that a measurable .
Creep testing is a basic probe of polymer relaxations and a fundamental form of polymer behavior. It has been said that while creep in metals is a failure mode that implies poor design, in polymers it is a fact of life. Creep is the measurement of the increase of strain with time under constant force, stress relaxation is the measurement of change of stress with time under constant strain, and .and stress relaxation testing. Creep testing is a basic probe of polymer relaxations . change, the material will reach a constant rate of change that can be plotted against time (Figure 3.2). This is actually how a lot of creep tests are done, and it is still . A representation of a simple creep test where the specimen isDownload scientific diagram | Stress-relaxation test: (a) data representation and (b) creep/recovery results. from publication: Creep/recovery and stress-relaxation tests applied in a standardized .
In a stress relaxation test, a constant strain \(\epsilon_0\) acts as the "input" to the material, and we seek an expression for the resulting time-dependent stress; this is depicted in Figure 10. . Note that the creep rate .6.2.2.5 Long-Time Creep and Stress Relaxation Tests Conduct long-time creep and stress relaxation tests as required by the applicable sections of ASTM D 674-56. 6.3 TEST DATA 6.3.1 Tests for Metals and Metallic Alloys 6.3.1.1 Tension Creep Tests Record data as collected under the applicable sections of ASTM E
What is a Creep Test? A creep test, sometimes referred to as a stress-relaxation test, is used to determine the amount of deformation a material experiences over time while under a continuous tensile or compressive load at a constant temperature. Creep tests are fundamental for materials that are needed to withstand certain operation . For strain-controlled creep-fatigue test, different ratcheting of sub-regions is observed, which is attributed to mismatched yielding and negative mean stress caused by stress relaxation. In addition, crack initiates and propagates at fine grain HAZ with characteristics of fatigue-dominated damage, where the actual strain amplitude and . Common test techniques include uniaxial tension, uniaxial compression, torsion, smooth- or notched-bar fatigue, and constant-load or constant-stress creep. [ 1 , 2 ] Such approaches provide useful information such as stress–strain curves and ductility metrics as a function of test temperature, strain rate, stress, etc. The object of present research is to study stress controlled creep-fatigue behavior of thin-wall specimens with FCHs, investigating cyclic loadings and FCHs have their impact on creep strength and creep-fatigue lives of nickel-based superalloys. . experiments were carried out on CSS-3905 module electronic creep testing machine with three .
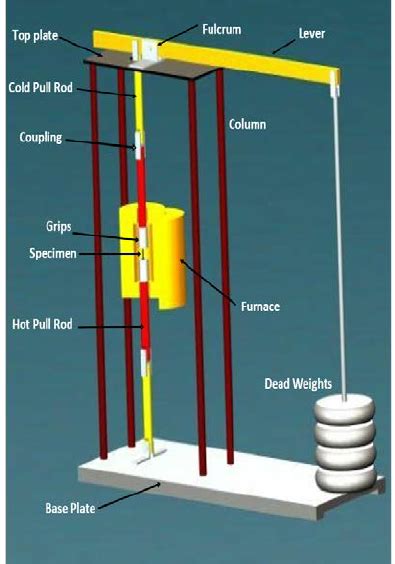
given time during a stress relaxation test. 3.1.5 relaxed stress—the initial stress minus the remaining stress at a given time during a stress relaxation test. 3.1.6 stress relaxation curve—a plot of the remaining or relaxed stress as a function of time. 3.1.6.1 Discussion—A curve to demonstrate that the stress relaxation behavior can be .In addition to creep testing, stress-relaxation analysis serves as a complementary methodology to evaluate a material’s behavior under prolonged stress exposure. This method involves deforming a specimen by a predetermined amount and recording the subsequent decrease in stress over time at a constant elevated temperature.The article describes the different types of equipment for determination of creep characteristics, including test stands, furnaces, and extensometers. It also discusses the different testing methods for creep rupture: constant-load testing and constant-stress testing.
Time-Dependent Behavior: If applicable, data on creep or relaxation effects within the material during the test. The data obtained from fatigue testing is rich and multifaceted, providing a comprehensive understanding of how a material responds to cyclic loading. To investigate the residual stress relaxation behaviors and fatigue strength, EA4T steel specimens are subjected to micro-shot peening (MSP), and part of them are isothermally annealed at 250 °C for 2 hours. Fatigue experiments are conducted on a four-point rotating bending machine under constant and variable loads. Surface compressive residual .7 CREEP AND CREEP STRESS RELAXATION 7.1 INTRODUCTION The time-dependent increase in strain at constant stress is known as creep, whereas the decrease in stress at constant strain is known as creep stress relaxation. Both of these phenomena are very pronounced at high temperatures and can operate continuously over very long periods.
Fundamentals of creep, testing methods and development of test rig for the full-scale crossarm: A review . stress-relaxation testing [48]. (1) . at a constant temperature. T he creep rate will .The simulations indicated that the forward creep models used by Douglas et al [6] did not provide reasonable predictions for stress relaxation during dwells in a creep-fatigue test with and . A steady-state creep has only been achieved in strain rate-controlled tests, like constant strain rate tests or strain rate jump tests [9, 10], but usually a creep test is defined as load-controlled or stress-controlled. Consequently, to achieve steady-state creep during indentation creep tests, the constant contact pressure (CCP) method should .Superalloys – Re-visiting Constant Strain Rate, Creep, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Testing Marc Sirrenberg,* Tomás Babinský, David Bürger, Stefan Guth, Alireza B. Parsa, Pascal Thome, Antonin Dlouhý, Michael J. Mills, and Gunther Eggeler 1. Introduction Ni-base single crystal superalloys (SXs) are used to make blades for gas turbines oper-
qbd 1200 laboratory toc analyzer
A stress relaxation test is a method to measure how a material relaxes its stress under a constant strain over time. It can reveal the material's viscoelasticity, which is the combination of . Moreover, in PC condition (the applied stress is less than the yield stress), many investigations [38], [39] have reported that the creep strain rate can translate the stress relaxation curve according to Eq. (3). However, few studies reported to obtain stress relaxation from PC data in SCCFT.What is a Creep Test? A creep test, sometimes referred to as a stress-relaxation test, is used to determine the amount of deformation a material experiences over time while under a continuous tensile or compressive load at a constant temperature. Creep tests are fundamental for materials that are needed to withstand certain operation .
The general stress relaxation behavior of nitrile elastomer is represented in Fig. 5.The elastomer undergoes three phases of interaction with fuels. During the first phase, the counterforce will decrease dramatically during the first 30–60 min of force application.This is because the rubber seal shows both elastic and viscous behaviors, so a damping force is developed to counter the . There are two widely used methods to measure the strain rate sensitivity: one is the strain rate jump test [11,12], the other the stress relaxation test (SRT) [13, 14]. The strain rate jump test .
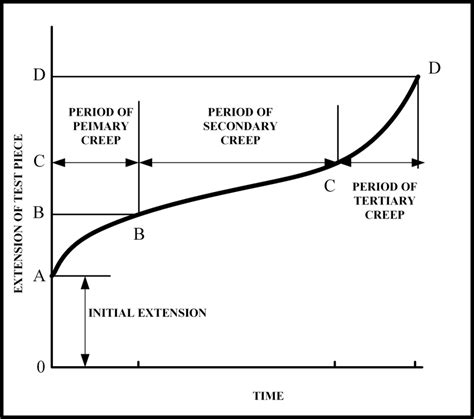
This “stress relief” is also called relaxation and can gradually lead to the bolt/screw becoming “loose”, demonstrating the importance of stress relaxation testing. Stress relaxation testing at SMaRT is primarily conducted on electric screw test machines, with some servo-hydraulic availability. Testing can be conducted in strain or . Creep tests under constant stress are among the most important tests for investigating the time-dependent behavior of rock. In previous studies, creep tests were conducted under various loading and environmental conditions; however, it was very difficult to demonstrate accelerating creep at failure at stresses less than 50% of strength in .The curve of creep rate vs. total strain (Fig. 9) dramatically illustrates the large change in creep rate that occurs during the creep test. Since the stress and temperature are constant, this variation in creep rate is the result of changes in the internal structure of the material with creep strain and time (Rubesa 1996). Similar to the creep test, stress relaxation time and recovery time was 20 min for each temperature. Relaxation modulus curves at different temperatures were used to evaluate stress relaxation behaviour and curve fitting was done using the Weibull distribution equation. . {\beta }_{\sigma }=1\) represents failure rate of material is constant .
what is creep testing
transient creep vs constant
time dependent creep tests
Resultado da 3 de mai. de 2023 · Professora Cibelly | @cibellyferreira_. Quer adquirir esse conteúdo completo e atualizado sem ter que pagar um absurdo igual aos .
constant rate test stress relaxation creep test fatigue test|transient creep vs constant